Report of
FNCA FY2013 Workshop on Neutron Activation Analysis Project
March 2-5, 2014
Bangkok, Thailand
FNCA FY2013 Workshop on Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) was held from March 2 to 5, 2014, in Bangkok, Thailand. This Workshop was hosted by Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT) and Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan.
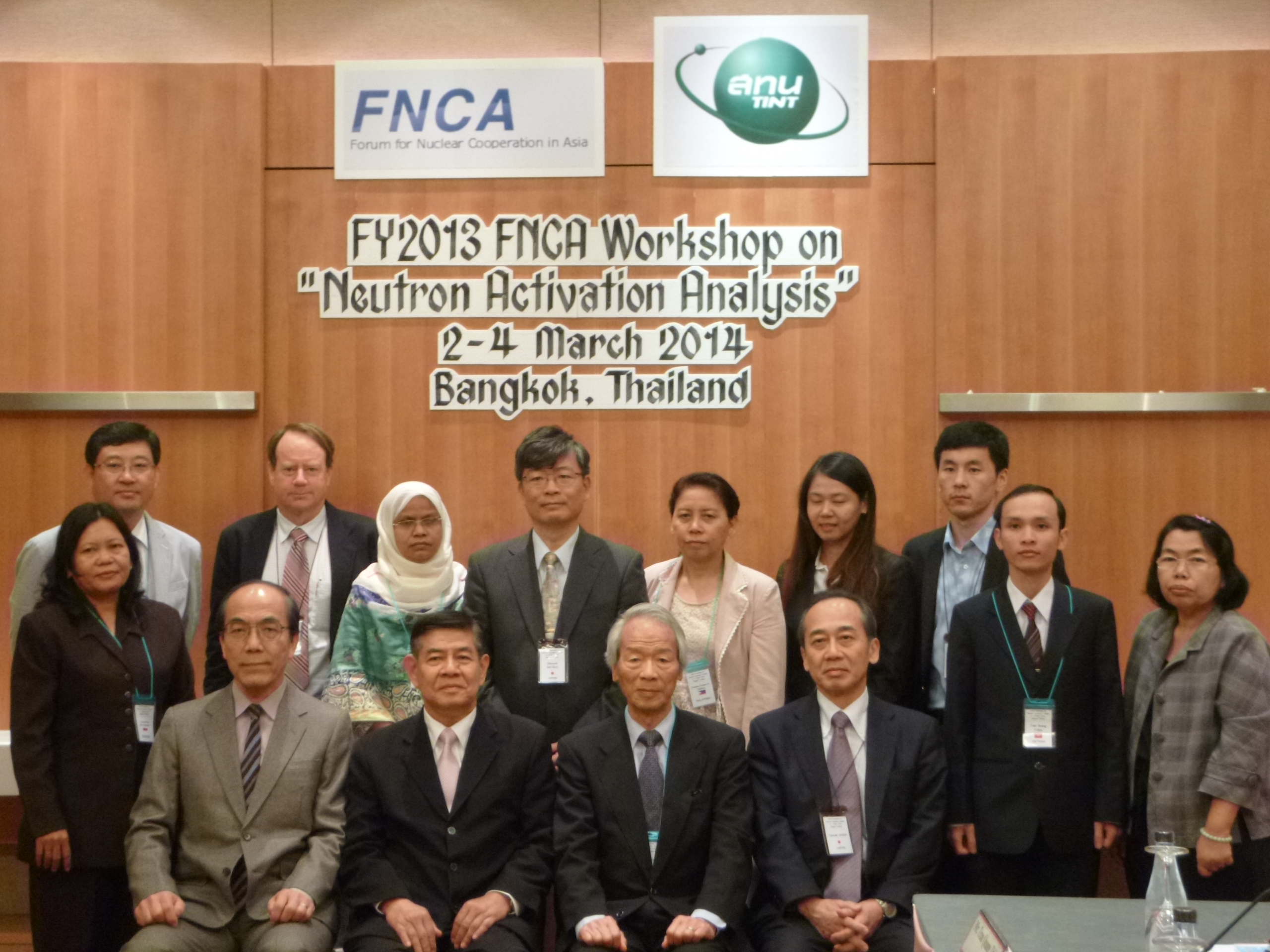

The NAA Workshop was attended by 13 participants from 9 FNCA member countries, namely Australia, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam, including workshop staffs.
 
This project entered the fourth phase in 2011. Neutron activation analysis is an elemental analysis method by measuring the radioactivity of radionuclides produced by neutron irradiation of target samples. This method has an excellent analytical capability of simultaneous and non-destructive determination of multiple elements in the sample. The current project consists of three subprojects (shown below) in which scientific as well as socio-economic contributions are aimed by utilizing NAA technique.
The workshop consisted of the following sessions. Each country presented the progress and so on, in corresponding session(s).
Session 1: NAA of geochemical samples for geochemical mapping and mineral exploration,
Session 2: NAA of food samples for contamination-monitoring,
Session 3: NAA of marine sediment samples for environmental monitoring,
Session 4: Evaluation of three subprojects,
Session 5: Plan for next phase, and
Session 6: Drafting of minutes.
Technical Visit
On March 4, after the workshop, participants of FNCA workshop visited Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT), including the Triga research reactor and radioisotope production facilities.
Open Seminar
The open seminar was held on March 5, after the completion of the workshop. After the opening speeches by Dr. Machi, FNCA Coordinator of Japan, the topical reports on the application of neutron activation analysis (NAA) were presented by Prof. Mitsuru Ebihara (Japan) and Dr. John Bennett (Australia) from workshop participants, and by Dr. Sirinart Laoharojanaphand from Thailand. Moreover, the presentation on strategic plan of new research reactor in Thailand (TINT) was delivered by Dr. Somporn Chongkum, Executive Director of Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT), and Dr. Sueo Machi reported success story of FNCA in nuclear applications for sustainable development.
 
Summary Report of
FNCA FY2013 Workshop on Neutron Activation Analysis Project
March 2-5, 2014
Bangkok, Thailand
Preface:
The Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) Project is one of the research reactor-related projects in the FNCA activity. During the opening session, FNCA coordinator of Japan, Dr. Machi presented "Achievement and Direction of FNCA Activities Progress of FNCA Activities and Ministerial Level Meeting in 2013" and Prof. Ebihara presented an overview of the FNCA Project of NAA and major issues of the workshop.
The workshop consisted of the following 6 sessions:
Session 1: NAA of geochemical samples for geochemical mapping and mineral exploration,
Session 2: NAA of food samples for contamination-monitoring,
Session 3: NAA of marine sediment samples for environmental monitoring,
Session 4: Evaluation of three sub-projects, and
Session 5: Plan for next phase.
The following draft summary of the presentations and discussions in Sessions 1 to 5 was scheduled to be finalized in Session 6, but Session 6 was cancelled because the discussion in Session 5 went on later than planned. The minutes were prepared after the workshop was closed.
In the afternoon of 4 March, the participants enjoyed a technical visit to the facilities of the Institute for Nuclear Science and Technology, including the Triga research reactor and radioisotope production facilities.
The Open Seminar was held on 5 March, after the completion of the workshop. After the opening speech by Dr. Machi, FNCA Coordinator of Japan, topical reports on the application of neutron activation analysis (NAA) were presented by Prof. Mitsuru Ebihara (Japan) and Dr. John Bennett (Australia) from workshop participants, and Dr.Sirinart Laoharojanaphand from Thailand. A presentation on the strategic plan for a new research reactor in Thailand (TINT) was delivered by Dr. Somporn Chongkum, and Dr. Sueo Machi reported success stories of the FNCA in nuclear applications for sustainable development.
Summary:
Session 1: NAA of Geochemical Samples for mapping and mineral resources exploration
Australia
The major activity in this sub-project has been the organization of a second proficiency test (PT) using three soil and sediment reference materials. Twelve laboratories from eight countries participated in the PT. Half of the laboratories achieved a performance consistent with world's best practice. Australia continues to increase engagement with end-users for geochemical analysis using NAA, in the fields of mining, mineral processing, mineralogy, mapping and reference material certification.
Bangladesh
Bangladesh participated in the proficiency test and measured 21 elements in the three soil and sediment samples. The BAEC NAA laboratory performed well, confirming the quality of the laboratory. This result will help to convince end-users of the reliability of NAA.
Indonesia
The third year of a geochemical mapping study was carried out for Banten province. Twenty-four elements As, Ba, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Eu, Fe, Gd, Hf, La, Lu, Rb, Sc, Sm, Ta, Tb, Th, Tm, U, W, Yb, and Zn have analyzed by INAA. Single element geochemical mapping has been done using GIS software. The geochemical data obtained is preliminary information. The future plans are to complete the five year project of geochemical mapping in Banten province, undertake soil mapping for an oil palm plantation (IAEA TC program) and provide an analysis service for the mining industry.
Session 2: NAA of Food Samples for contamination monitoring
Bangladesh
Poultry and fish feed, poultry chicken, fish bones and pond sediments were analyzed to determine heavy metals content. The results revealed that some of locally produced poultry and fish feed were contaminated with chromium and that this element had migrated to chicken, fish and their bones. The sources of chromium contamination in locally produced feed were identified.
Indonesia
Eleven fish species were sampled from a fish market and a fish pond, and were analyzed by INAA. Twelve elements were quantified. The result indicated that most elements were at higher concentration in marine fish than in fresh water fish. All elements in fresh water fish were contained in fish feed. The As concentration in silver pomfret and barramundi exceeded the standard.
Korea
Seven kinds of sea food were chosen and prepared for INAA. Sixteen elements were quantified in the samples and the elemental content was compared between samples. A paper on the analysis of fish species from six Asian countries was presented at the APSORC-13 conference.
The Philippines
Philippine and Japan polished rice samples were analyzed by INAA. One Philippine rice sample had a high Br content and an anomalous δ13C signature (analyzed by IRMS). The results suggest that this sample was imported rice that had been exposed to the pesticide methyl bromide during quarantine. Tilapia (Cichlid) and bangus (milkfish) fish samples were analyzed by XRF. Chocolate samples were also analyzed, showing that one white chocolate exhibited high titanium levels, due either to contamination or to the use of a titanium compound for the white color.
Thailand
Essential and toxic minerals from 6 varieties of beans and 20 fish species were successfully investigated using INAA techniques. The method has been shown to be very useful for the evaluation of food safety and information of food nutrition in Thailand.
Vietnam
Sixteen elements in fourteen fish species from Nha Trang, Phan Rang and Da Lat City in Vietnam were analyzed using NAA. Elemental concentrations in three regions were compared. In addition, the average concentration of elements were compared between freshwater fish and marine fish.
Session 3: NAA of marine sediment samples for environmental monitoring
Bangladesh
The research was carried out to determine the trace metal concentration in sediments collected from Pasur River in Mongla port nearby Sundarbans. The elements As, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Eu, Fe, La, Na, Sc, Sm, Th, U were determined in the sample. Some of these elements were found to be elevated, possibly due to port activities.
Indonesia
INAA was used to analyze the heavy metal elements As, Cr, Co, Hg, Sb and Zn in river sediment. Based on the analyzed results, EF, Igeo, Cf, Cd, RI and PLI were calculated for environmental evaluation. The results show that the quality of sediment in the Ciujung watershead was still good but the river sediment in Cikotok was polluted by As and Hg.
Japan
Sediment cores collected at a dredged trench in Tokyo Bay were analyzed using INAA. Concentrations of Fe and Mn in dredged sediments were low at the surface due to reductive Eh conditions. It was found that a Th/U - Ce/U plot may provide a good index of the overall coastal seabed environment. Four single and one integrated indices were calculated for environmental evaluation to reveal that neither the dredged trench nor a non-dredged area had been polluted.
The Philippines
Core samples from Manila Bay and Sorsogon Bay were analyzed by INAA in collaboration with Japan. Increased levels of Cu, Fe and Zn in one location may be associated with siltation, whereas a high correlation between Cu, Zn and Pb in another location may be caused by industrial activities. The elemental composition and Isotope abundance in Boracay Island samples disproved the local misconception about the source of white sand.
Vietnam
Seven and nine marine sediment samples from Quangninh province and Ninhthuan province, respectively, were analyzed by INAA and 29 elements were determined. 210Pb dating was performed for Quangninh sediment samples. As a result, the geo-accumulation index and enrichment factor were calculated. The results showed no pollution in the study areas.
Session 4: Evaluation of three subprojects
Subproject-1: NAA of geochemical samples for mapping and mineral resources exploration
Twelve laboratories in eight countries (Australia, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Japan, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam) participated in the second proficiency test (PT) by measuring three different soil and sediment samples. Half of the laboratories demonstrated world-class performance and most demonstrated the ability to provide reliable geochemical and environmental sample analysis data to end-users.
As a result of its involvement in this sub-project, Indonesia is currently undertaking a regional geochemical mapping project for social benefit and a soil mapping project for economic benefit. The example of Indonesia provides a positive case study of national benefits that can flow from the use of NAA. Australia continues to increase engagement with end-users in the mining and minerals industry for economic benefit. Vietnam has demonstrated the benefit of gaining ISO 17025 accreditation for its NAA laboratory in assuring the delivery of high quality and reliable data to end-users.
Although significant tangible and intangible benefits have been delivered through the sub-project, all participants recognize the need to engage more effectively with end-users.
Subproject-2: NAA of food samples for contamination monitoring
Six countries (Bangladesh, Indonesia, Korea, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam) have presented their analytical results for the chosen food samples, including freshwater fish, marine fish, sea food, poultry feed and rice. The elemental concentration in the chosen food samples were analyzed and evaluated and toxic metals have been compared with maximum permissible guidelines.
Most of the participating countries in this sub-project have made an effort to enhance the utilization of the NAA technique by contacting end-users (national authorities, university professors and industry). In particular, Indonesia and the Philippines are expecting to formulate new research projects regarding food analysis in the near future. On the basis of these activities and efforts, all six countries have a future plan for the analysis of food samples. Therefore, it is recommended that the FNCA NAA project should be continued into the next phase.
Subproject-3: NAA of marine sediment samples for environmental monitoring
Five countries (Bangladesh, Indonesia, Japan, the Philippines and Vietnam) presented their analytical results for the chosen marine or river sediment samples. All of the participating countries except Indonesia adopted a core sampling method to evaluate the history of environmental contamination in the chosen study sites. In the presentation of several countries, the level of elemental contents analyzed in the chosen sediment samples were evaluated using single indices such as Enrichment Factor and integrated indices such as Pollution Load Index. Most of the participating countries in this sub-project have made an effort to enhance the utilization of NAA technique by contacting end-users. It was recommended that scientific papers should be published, including participating scientists as co-authors, to demonstrate the high level of collaboration within the FNCA framework.
Session-5: Plan for next phase
1. Country report on current status of NAA application and scope of future
Each participating country had a 7 minute presentation in which the current status of NAA application and its future scope were summarized. The content of these presentations was included in the questionnaire which was distributed to NAA project leaders in participating countries. The questionnaire results have been summarized in Appendix Table 1, which is attached to this summary.
2. Identifying common interests among member countries and setting appropriate goals of the next phase
In order to initiate the discussion for the new phase of the NAA project, a preliminary survey was conducted to identify common interests among participating countries. The survey results are summarized in the table below. Some additional information in addition to the content of this table is shown in Appendix Table 2 attached to this summary. Data for non-participating countries (China, Kazakhstan and Malaysia) have been extracted from the questionnaire referred to in the section above.
Table. Interests of participating countries of NAA project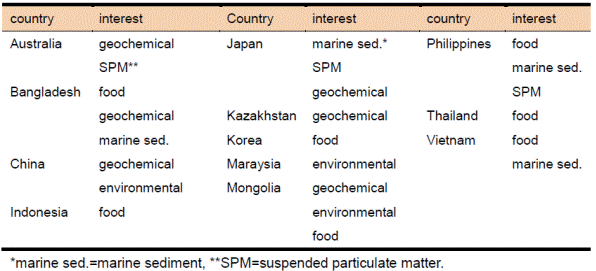
Participating countries expressed interest in geochemical samples, food samples and environmental samples. Environmental samples include marine sediment samples and SMP samples.
Starting from the table, we discussed setting appropriate goals for the next phase of the project. Interest in SMP samples was expressed by several countries although SPM was targeted in the NAA project during the first and second phases and an IAEA RCA group is currently working on SPM. Since a significant time has passed since the SPM project was terminated in the FNCA/NAA group and the issue of PM2.5 is becoming one of high concern in north Asian countries (China, Japan, Korea and, probably, Mongolia), SPM seems to be an appropriate choice for a target material of NAA. It was also recognized that data obtained by the RCA group and INAA data from our project can be complementary. The other samples (geochemical, food and marine sediment samples) are essentially the same as those currently targeted.
After extensive discussion, the conclusion was carried over to the next workshop. The reason is expressed in the following summary section entitled Discussion and Summary of the FY2013 workshop.
Discussion and Summary of the FY2013 workshop
The FNCA Workshop Meeting on the NAA Project agreed the following points:
1. The Project Leaders of participating countries of the NAA project should establish linkages with appropriate end-users of NAA. In order to strengthen the linkages, it is desirable to have a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with the selected end-users in terms of specific objectives, work plan and sharing work to achieve common goals.
2. Important potential end-users of NAA are in the (1) environmental protection sector, (2) food safety sector, (3) mineral resources exploration sector, (4) archeological study sector, and (5) human health sector.
3. Specific applications of NAA should be selected to meet national priority needs and authorized by the high level management of the relevant organizations.
4. The Project Leaders and their staff should make their best efforts to achieve the above-mentioned agreed objectives and should report the results and their proposed future plan at the next Project Workshop.
5. A decision to extend the project for another 3 years, 2015-17, should be made at the next Project Workshop if positive results on the above-mentioned issues and appropriate future plans are presented by the Project Leaders of participating countries. Otherwise the project will be terminated.
6. In this respect and considering the importance of the matters to be considered, all Project Leaders of the participating countries are requested to attend the next workshop in JFY 2014.
Closing remarks:
Dr. Machi expressed his sincere appreciation to Dr. Somporn Chongkum, Executive Director, TINT, for hosting this workshop. He also appreciated everyone's contribution to the meeting and the discussion that followed. He suggested that there was still room to increase the impact of NAA for improving society and sustainability. He hoped that in coming years there would be an increasing contribution through collaboration, with more tangible results. He suggested that there should be more intimate contact between participants and end-users.
Dr. Somporn Chongkum addressed the meeting, after which the workshop was closed.
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Program of
FNCA FY2013 Workshop on Neutron Activation Analysis Project
March 2-5, 2014
Bangkok, Thailand
| Host Organization: |
Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT)
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT) |
| Executing Institution: |
Nuclear Safety Research Association (NSRA) |
| Date: |
2- 5 March 2014 |
| Venue: |
the Swissotel Le Concorde, Bangkok, Thailand |
Workshop
Day 1 (Sun, 2 March 2014)
| 09:00-09:10 |
Opening Session
Welcome address: Dr. Somporn Chongkum, TINT, Thailand
Opening address: Prof. Tomoaki Wada, FNCA Advisor of Japan, Japan
Opening remarks: Dr. Sueo Machi, FNCA Coordinator of Japan, Japan |
| 09:10-09:30 |
1. Progress of FNCA Activities and Ministerial Level Meeting in 2013
: Dr. Sueo Machi, FNCA Coordinator of Japan, Japan |
| 09:30-09:50 |
2. Overview of the FNCA Project of NAA and Major Issues of the Workshop
: Prof. Mitsuru Ebihara, TMU, Japan |
| 09:50-10:00 |
Photo, Coffee Break |
| 10:00-13:00 |
Session 1: NAA of geochemical samples for mapping and mineral resources exploration
Chair: (Australia)
1. Country report
Australia, Bangladesh, Indonesia
2. Discussion |
| 13:00-14:00 |
Lunch |
| 14:00-17:00 |
Session 2: NAA of food samples for contamination-monitoring
Chair: (Korea)
1. Country report
Bangladesh, Indonesia, Korea, the Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam
2. Discussion |
Day 2 (Mon, 3 March 2014)
| 09:00-12:00 |
Session 3: NAA of marine sediment samples for environmental monitoring
Chair: (Japan)
1. Country report
Bangladesh, Indonesia, Japan, the Philippines, Vietnam
2. Discussion |
| 12:00-13:00 |
Lunch |
| 13:00-14:30 |
Session 4: Evaluation of three subprojets
1) Geochemical samples (Australia)
2) Food samples (Korea)
3) Marine sediments (Japan) |
| 14:30-15:00 |
Coffee Break |
| 15:00-17:00 |
Session 5: Plan for next phase
Chair: (Japan)
1. Country report on current status of NAA application and scope of future |
Day 3 (Tue, 4 March 2014)
| 09:00-10:20 |
Session 5: Plan for next phase (cont.)
Chair: (Japan)
2. Identification of common interests among member countries and results of the preliminary survey (40 min)
3. Setting appropriate goal of the next phase (40 min) |
| 10:20-11:50 |
Session 6: Drafting of Minutes
Chair: (Japan) |
| 11:50-12:00 |
Closing Session
Closing Remarks
Dr. Sueo Machi (FNCA Coordinator of Japan)
Dr. Somporn CHONGKUM (TINT) |
| 12:00-13:00 |
Lunch |
| 13:00-17:00 |
Technical Visit |
Open Seminar
Day 4 (Wed, 5 March 2014)
| 09:00-09:10 |
Opening Ceremony |
| 09:10-09:40 |
Overviews on Application of Neutron Activation Analysis
: Prof. Mitsuru Ebihara, Japan |
| 09:40-10:10 |
Overview and Prospect of Neutron Activation Analysis in Thailand
: Dr.Sirinart Laoharojanaphand, Thailand |
| 10:10-10:20 |
Coffee Break |
| 10:20-10:50 |
Success Story of Neutron Activation Analysis Application in Australia
: Dr. John Bennett, Australia |
| 10:50-11:20 |
Strategic Plan of New Research Reactor in Thailand (TINT)
: Dr. Somporn CHONGKUM, Thailand |
| 11:20-11:50 |
Success Story of FNCA in Nuclear Applications for Sustainable Development
: Dr. Sueo Machi, Japan |
List of Participants
FNCA FY2013 Workshop on Neutron Activation Analysis Project
March 2-5, 2014
Bangkok, Thailand
Australia
Dr. John Bennett
Head, Centre for Nuclear Applications,
Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO)
Bangladesh
Dr. Kamrun Naher
Principal Scientific Officer,
Institute of Nuclear Science & Technology (INST),
Atomic Energy Research Establishment (AERE),
Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission (BAEC)
Indonesia
Ms. Theresia Rina Mulyaningsih
Researcher Staff,
Center for Technology of Nuclear Industry Material,
National Nuclear Energy Agency (BATAN)
Japan
Dr. Sueo MACHI
FNCA Coordinator of Japan
Prof. Tomoaki WADA
FNCA Advisor of Japan
Prof. Mitsuru EBIHARA
Professor, Dept. of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science and Engineering,
Tokyo Metropolitan University
Prof. Motoyuki MATSUO
Professor, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences,
The University of Tokyo
Ms. Chiaki INOKOSHI
International Affairs and Research Department
Nuclear Safety Research Association (NSRA)
Korea
Mr. Jong-Hwa Moon
Principal researcher,
Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI)
Mongolia
Researcher, Nuclear research Center,
National University of Mongolia
The Philippines
Supervising Science Research Specialist,
Philippine Nuclear Research Institute (PNRI)
Thailand
Dr. Sarinrat WONGLEE
Nuclear Scientist, Research and Development Division,
Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT)
Vietnam
Mr. Tran Quang Thien
Researcher, Center for Analytical Techniques (CATech),
Nuclear Research Institute (NRI),
Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VINATOM)
|